Ever wondered when you visit a website, why certain components of the websites are working but others are not? How does a system prevent itself from crashing under heavy load? How a system can handle a sudden spike in traffic?
The answer is load shedding. Load shedding is a technique to scale down the resources of a system to prevent it from crashing under heavy load. In this article, we will discuss how load shedding works and how to implement it in a microservices architecture.
Before we dive into load shedding, let's understand the basics of microservices architecture.
You can directly jump to the section on Load Shedding if you are already familiar with microservices architecture.
Overview of microservices
Microservices architecture divide a complex system into smaller, manageable services. Each service is responsible for a specific task and can be deployed independently. This makes system more scalable, flexible and easier to maintain.
Microservices architecture is widely used by companies like Google, Netflix, Amazon, Uber, etc. This architecture allows companies to scale their system as per the demand.
Microservices architecture is a great choice for large, complex applications that have a lot of traffic but it is not suggested for small applications as it adds complexity to the system and it is expensive to maintain.
Example of microservices architecture
Let's take an example of a food delivery application like Zomato, Swiggy or DoorDash.
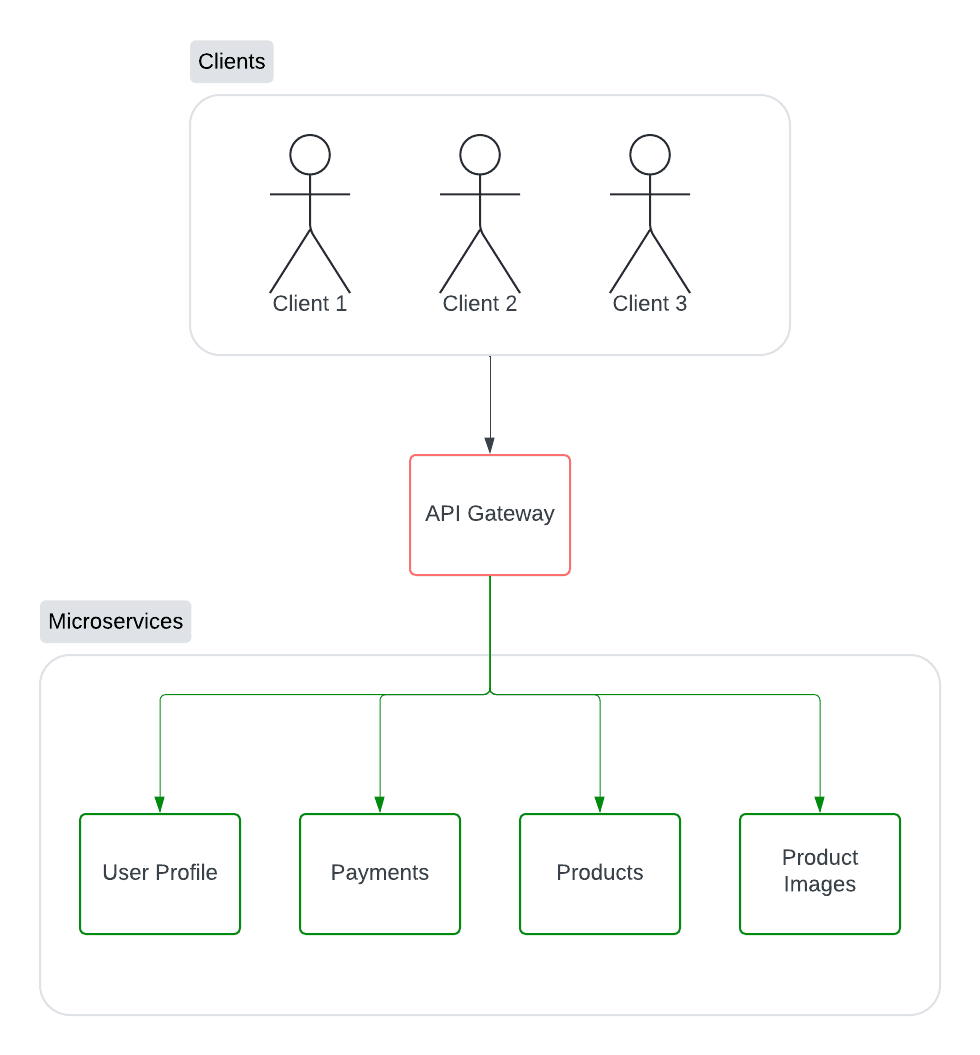
The application can be divided into following services:
- User Profile
- Payments
- Products
- Product Images
When a user visits the application, the request is routed to the API Gateway which then routes the request to the respective service. User Profile service is responsible for managing user profiles, Payments service is responsible for managing payments, Products service is responsible for managing products and Product Images service is responsible for managing product images.
Each service can be deployed independently and can be scaled as per the demand. This makes the system more scalable and flexible. If the Products service is getting a lot of traffic, it can be scaled independently without affecting other services.
Advanced architecture of microservices

Now after adding basic microservices, we need more tools to manage the system and make it more scalable.
We have added 3 more services to the system:
- Monitoring and Logging: This service is responsible for monitoring the system and logging the events. It helps in identifying the issues in the system.
- Service Registry: This is a database of all the services in the system. It helps in routing the request to the respective service.
- Simple Storage Service: Also known as AWS S3, this is an object storage bucket where all the product images are stored.
Now that we have understood the basics of microservices architecture, let's dive into load shedding.
What is Load Shedding?
Load shedding is the practice of sacrificing enough application traffic to keep partial availability in the presence of an overload condition. Used in conjunction with strategies like load balancing, load shedding helps applications support service level agreements (SLAs) when increased traffic overwhelms available system resources.
To understand this better, let's prioritize the services in the food delivery application.
- User Profile: User Profile service is the most important service as it is responsible for managing user profiles. If the User Profile service is down, the user will not be able to login to the application.
- Payments: Payments are the second most important service as it is backbone of any business.
- Products: Products service is the third most important service as it is responsible for managing products.
- Product Images: Product Images service is the least important service as it is responsible for managing product images.
Now let's say the system is under heavy load and we can't add more instances to the system. In this case, we can shed (shut down) the least important service i.e. Product Images service to prevent the system from crashing.
We will reallocate the resources of Product Images service to the Payments service so that the system can handle the load.

This is what load shedding looks like in a microservices architecture.
Conclusion
Load shedding is a technique to scale down the resources of a system to prevent it from crashing under heavy load. It is a great way to handle sudden spikes in traffic and keep the system up and running.